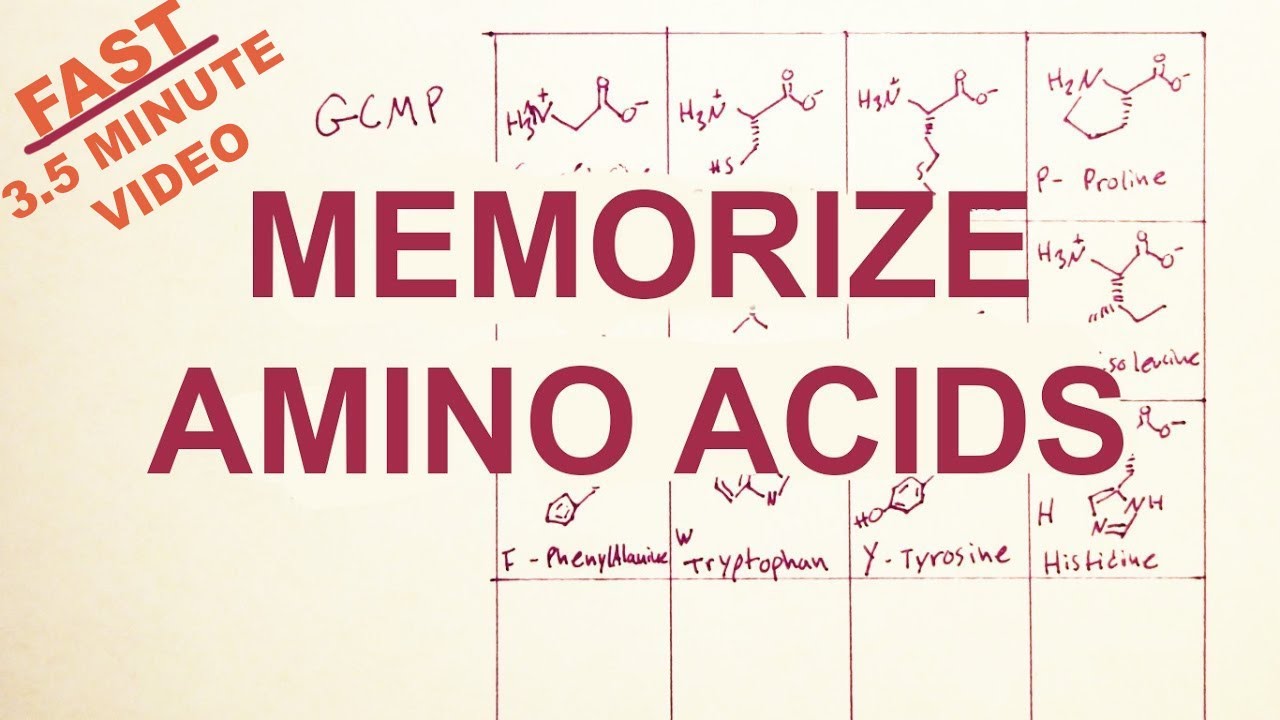
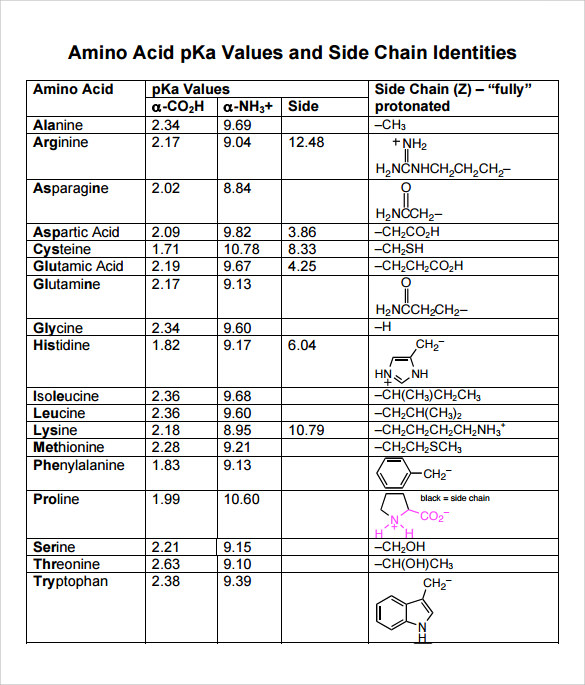
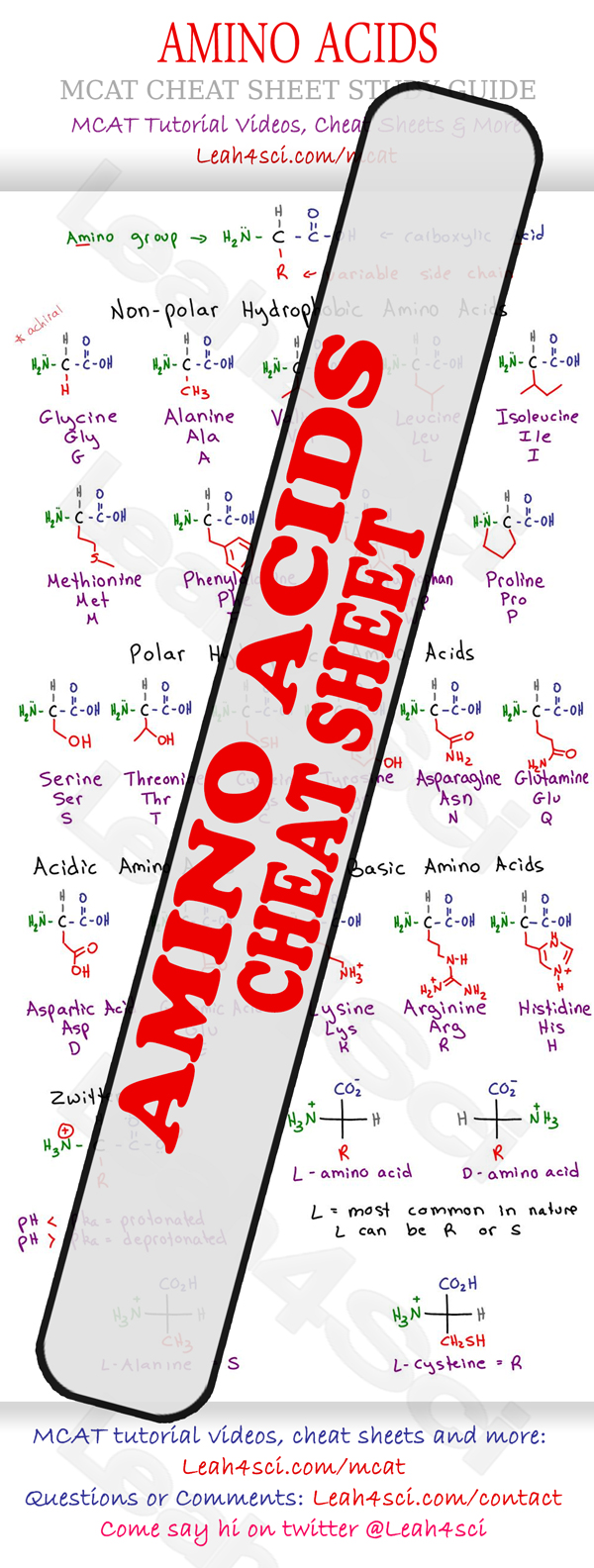
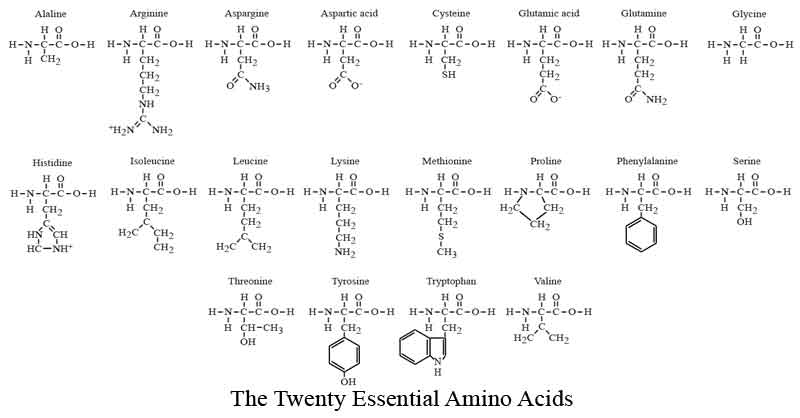
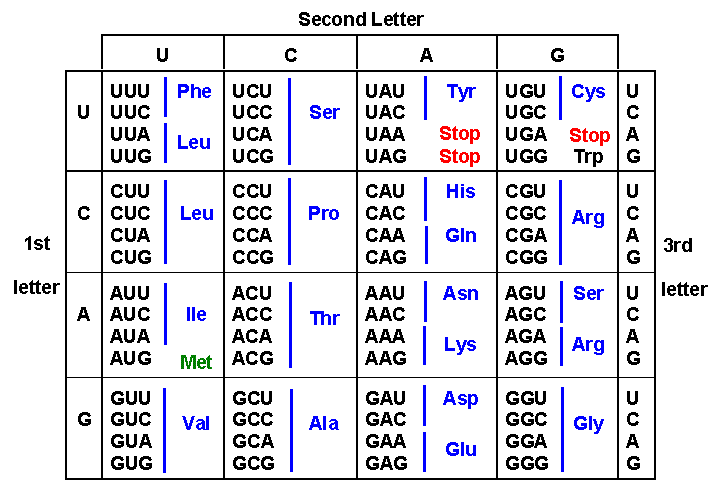
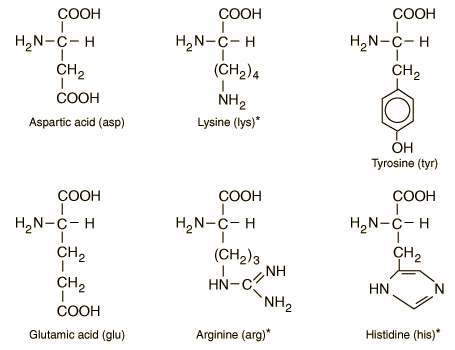Amino Acid Structure Chart
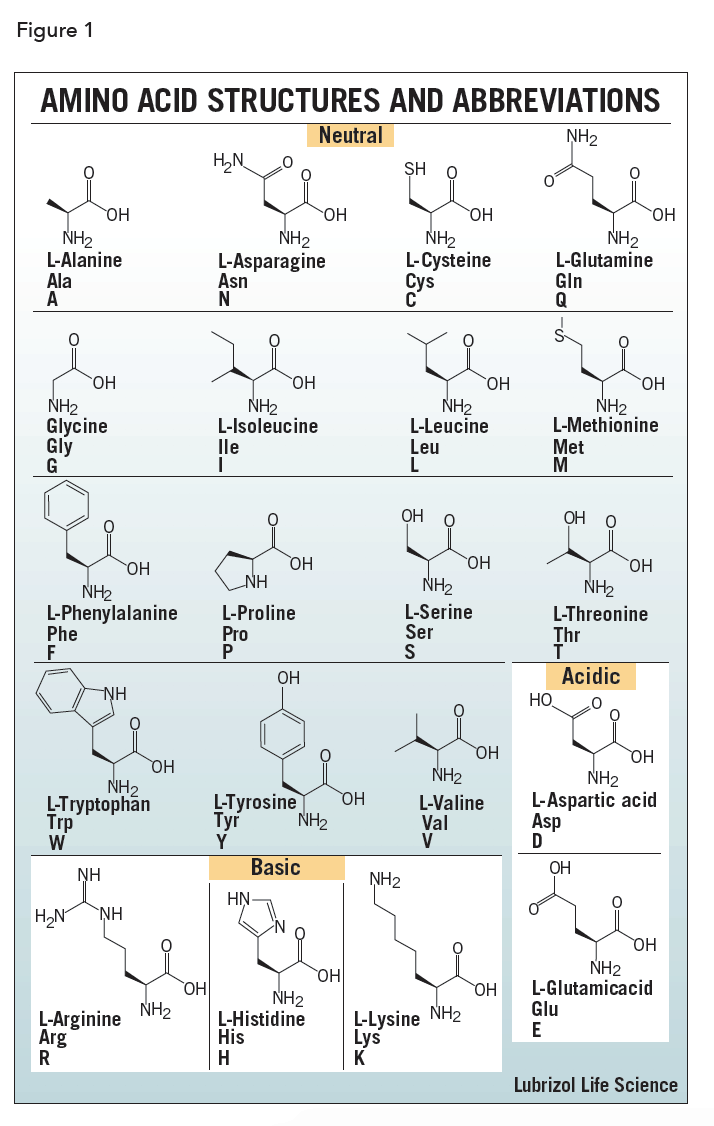
Amino acid structure chart and reference table amino acids are the backbone of peptides and proteins.
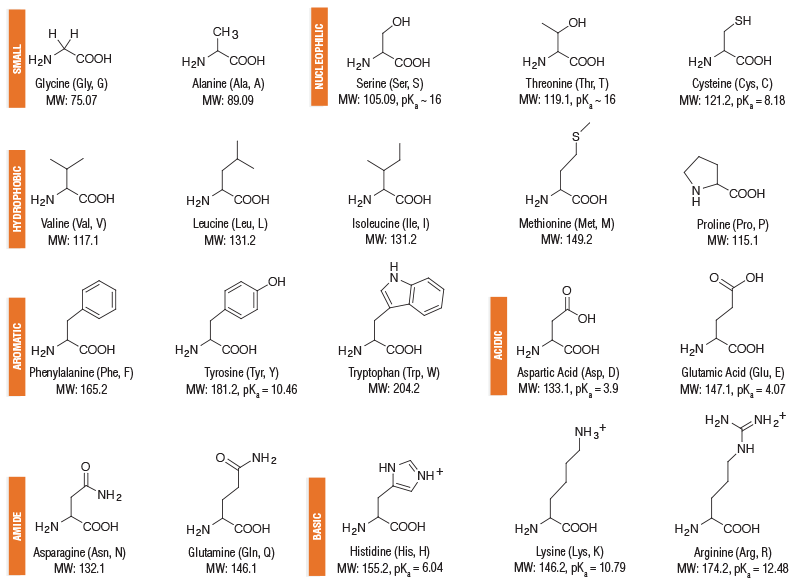
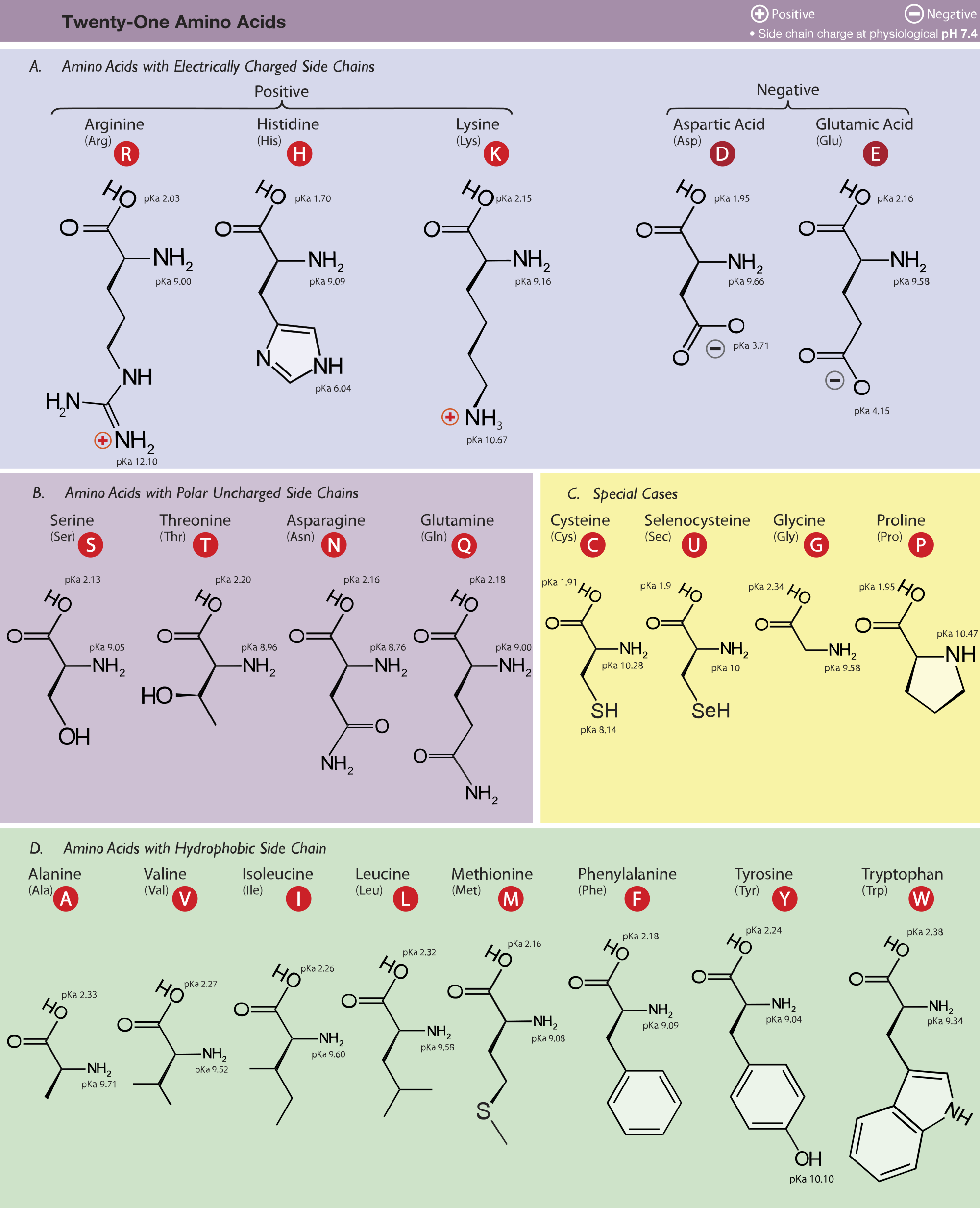
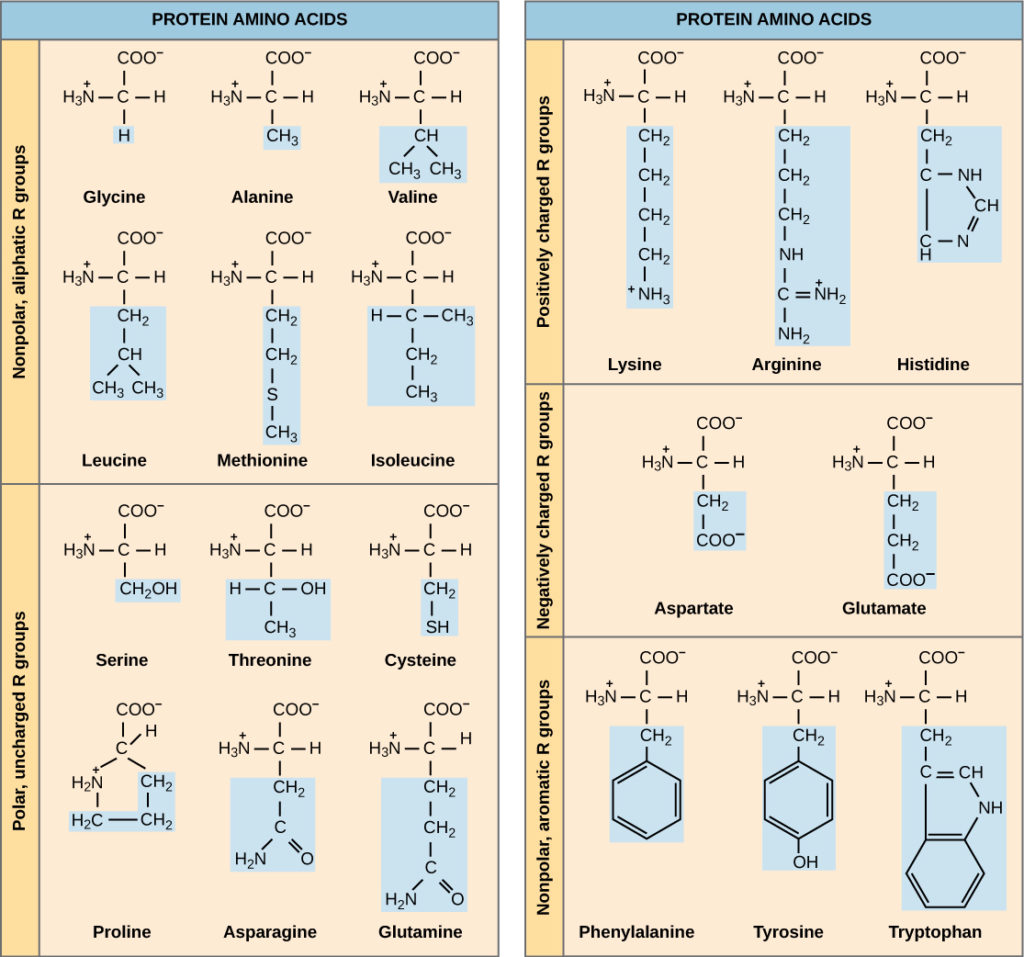
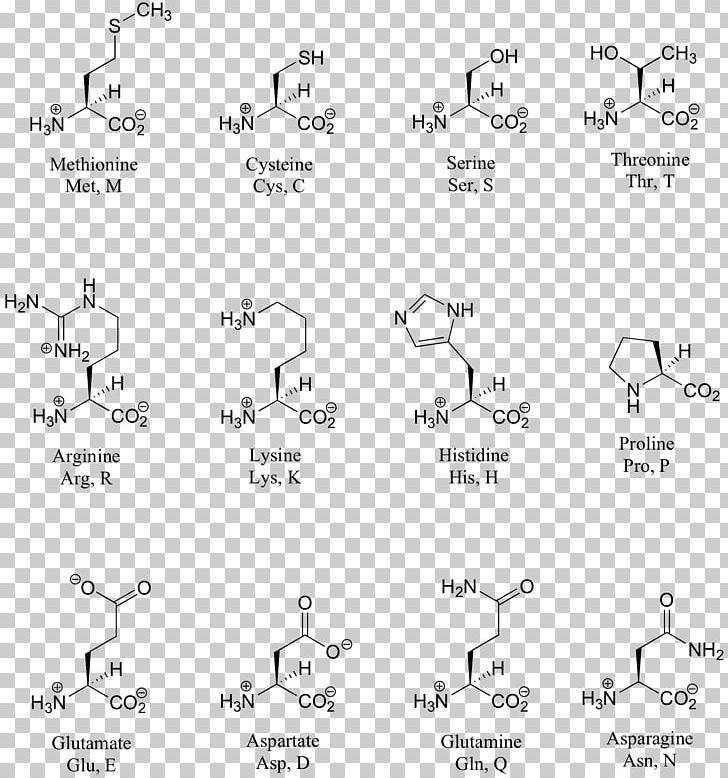
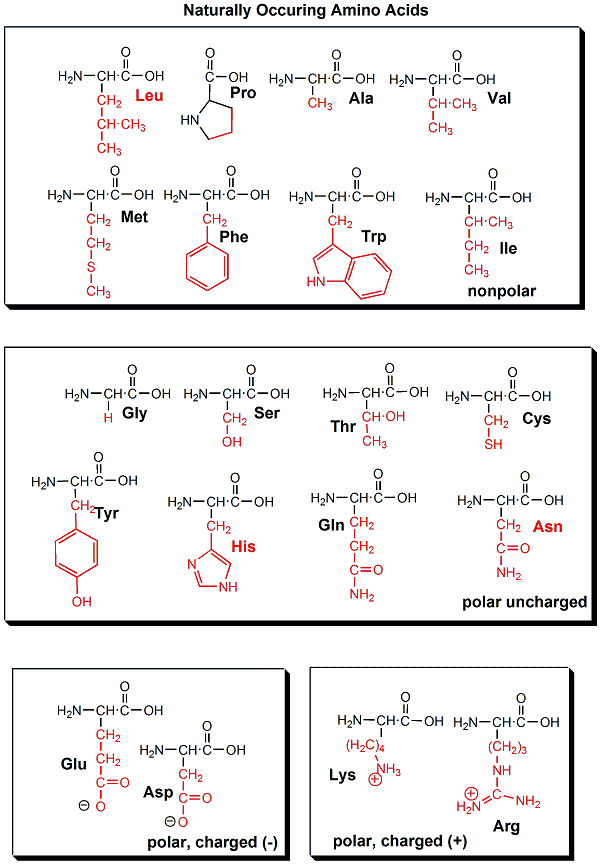
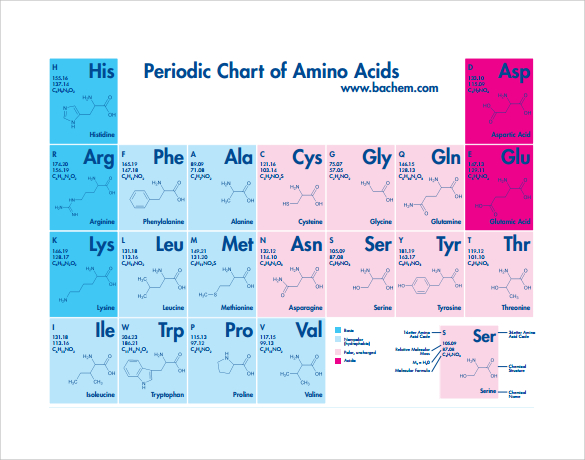
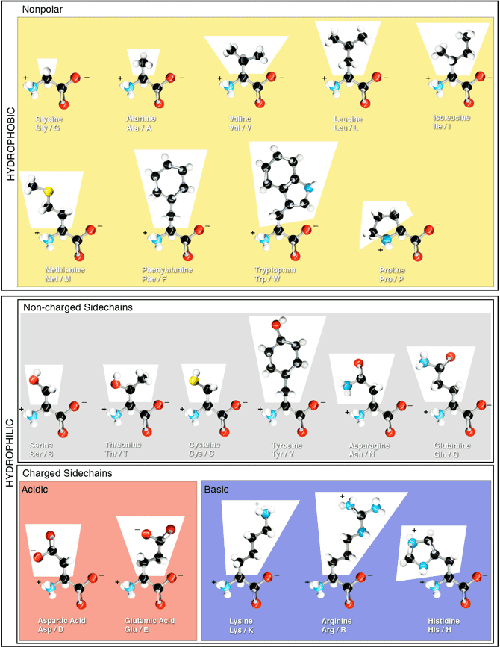
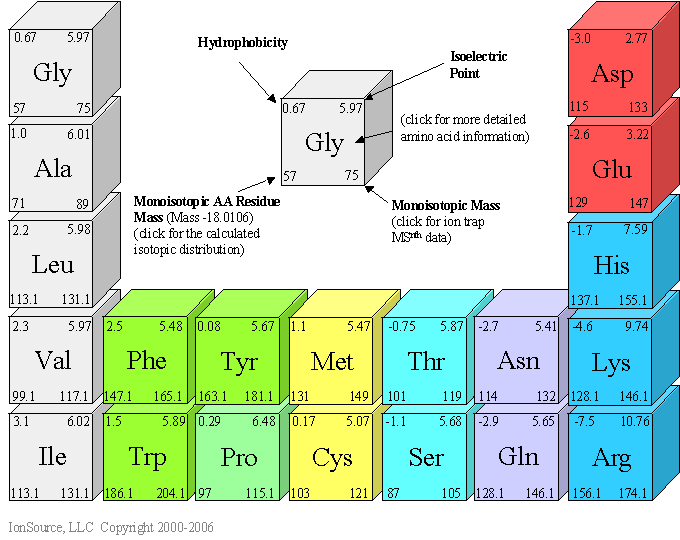
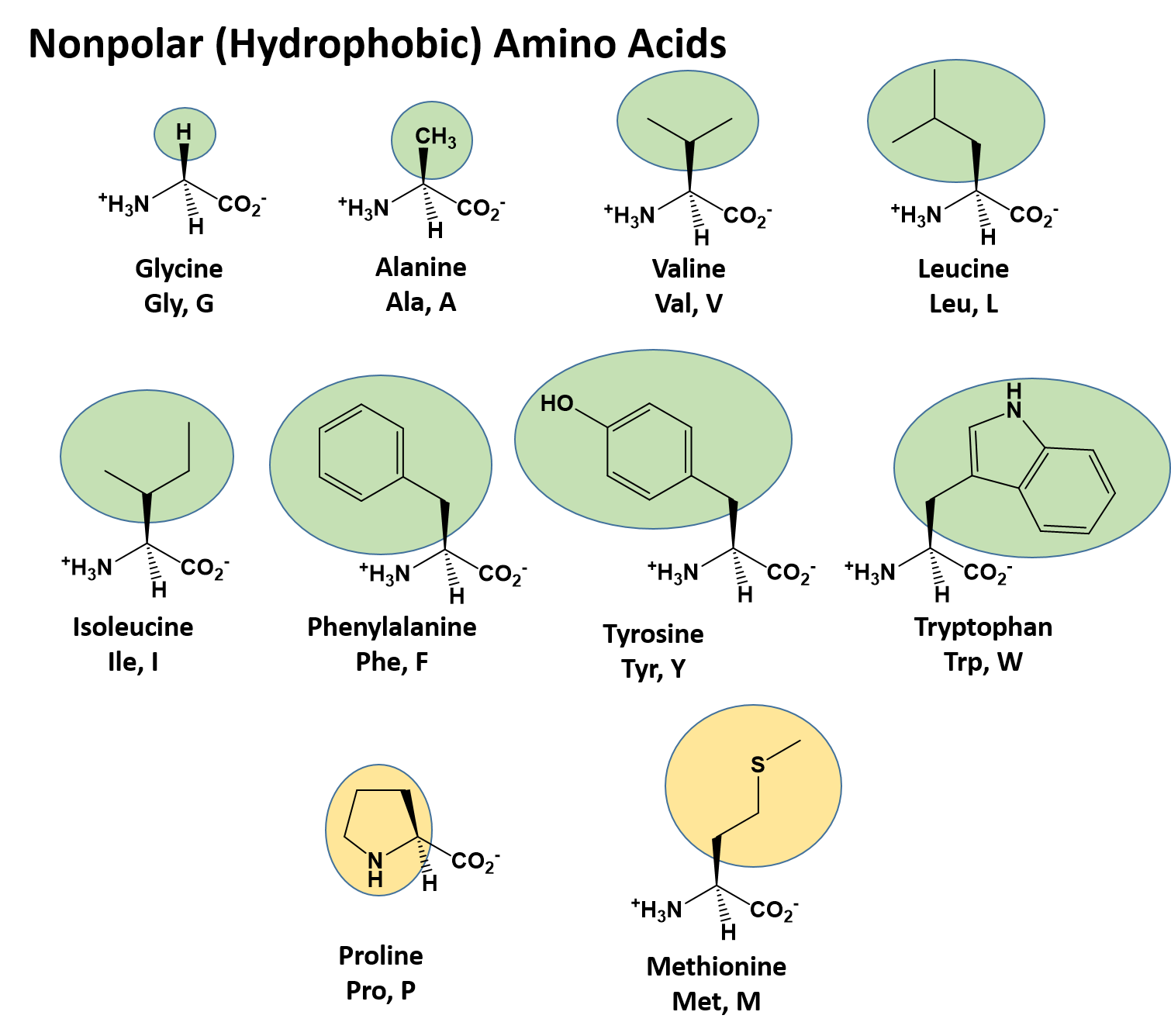
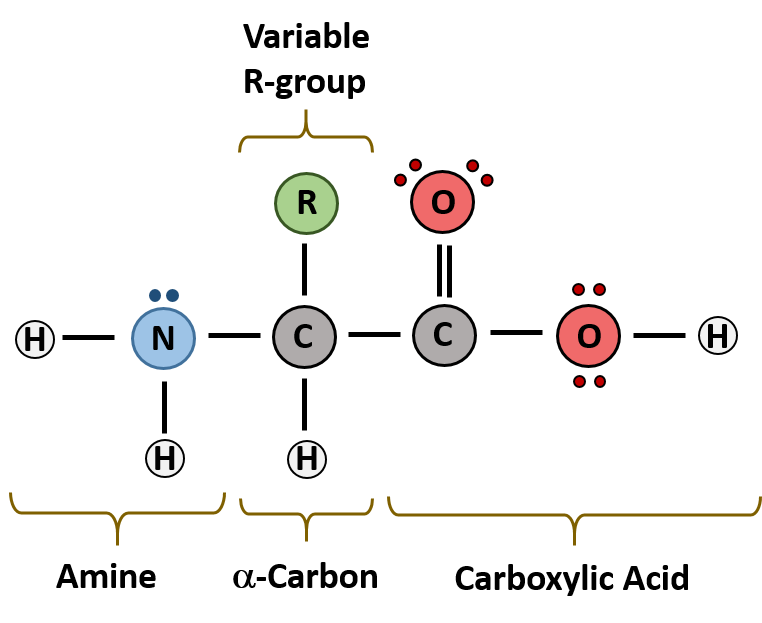
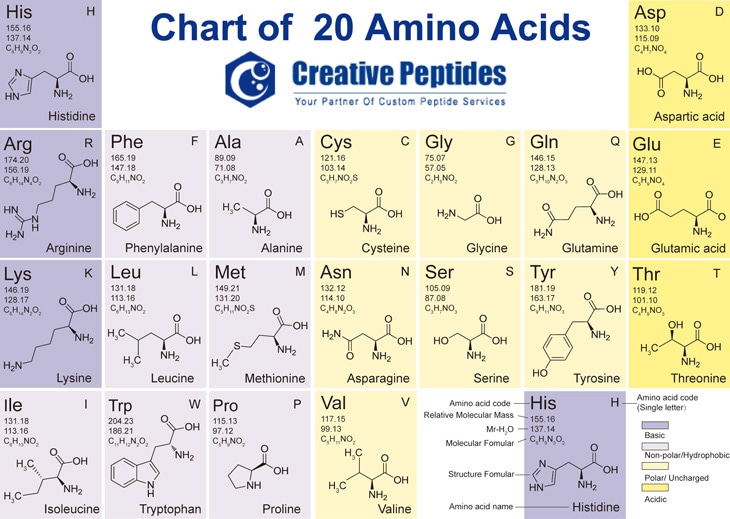
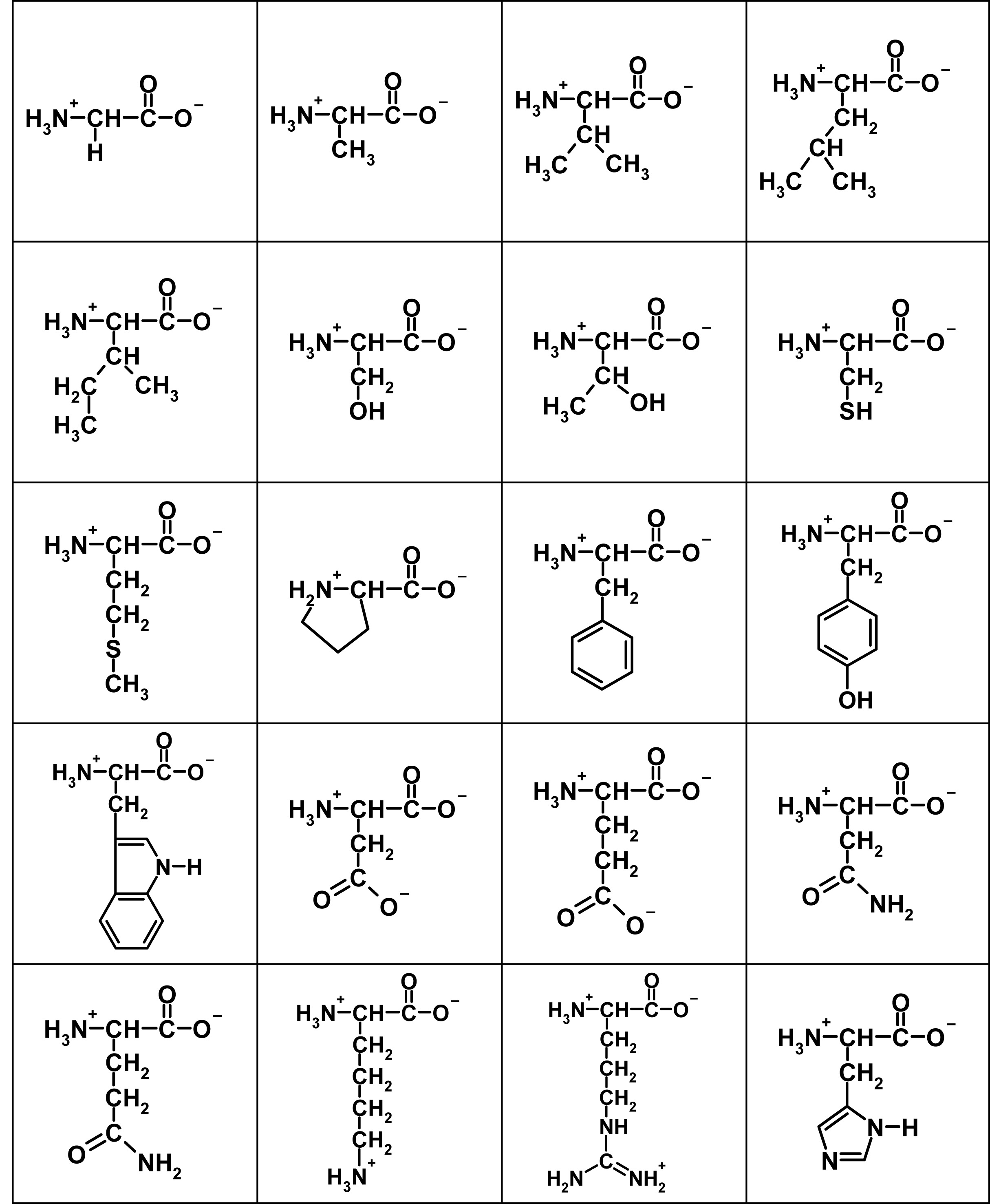
Amino acid structure chart. 1 non polar and neutral 2 polar and neutral 3 acidic and polar 4 basic and polar. A higher score indicates that. Each amino acid is structured from an amino group and a carboxyl group bound to a tetrahedral carbon.
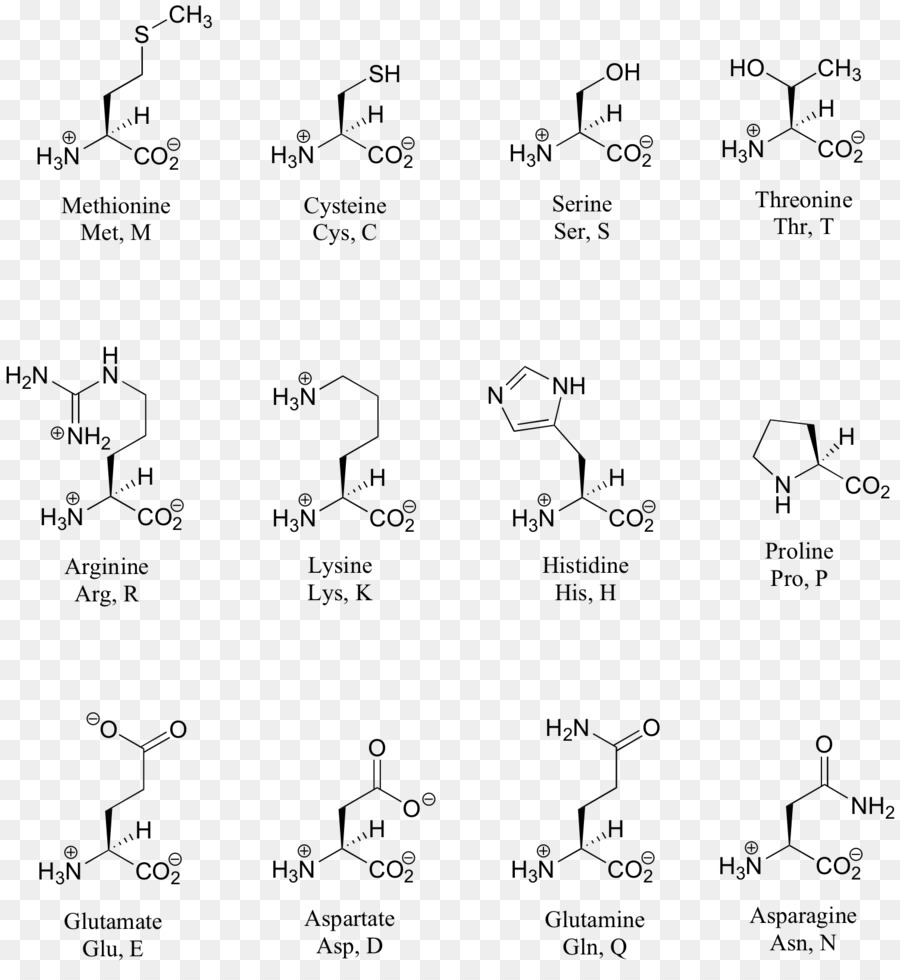
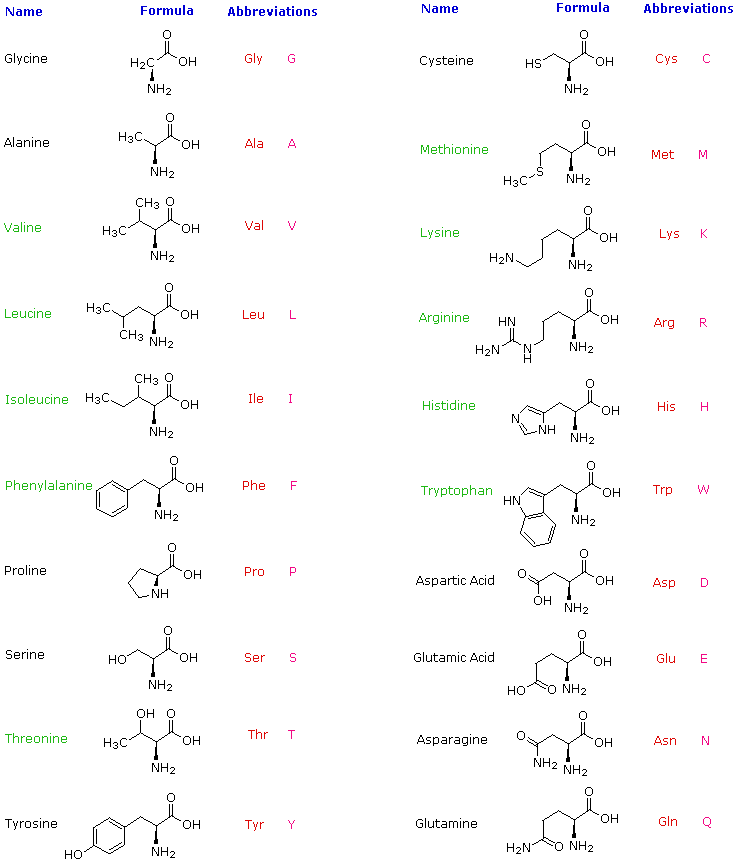
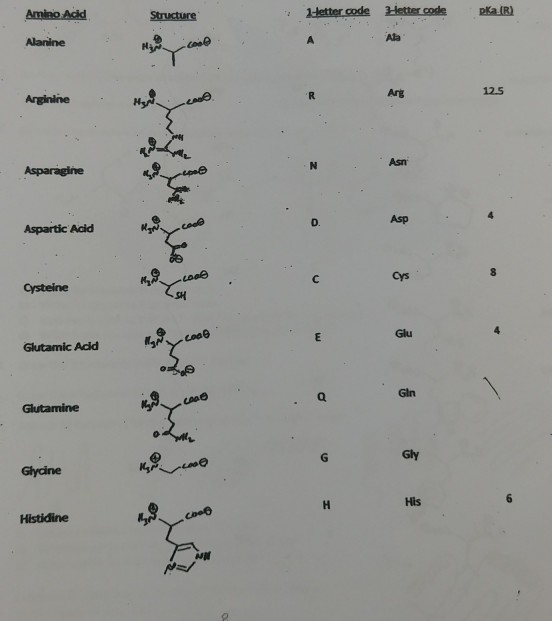
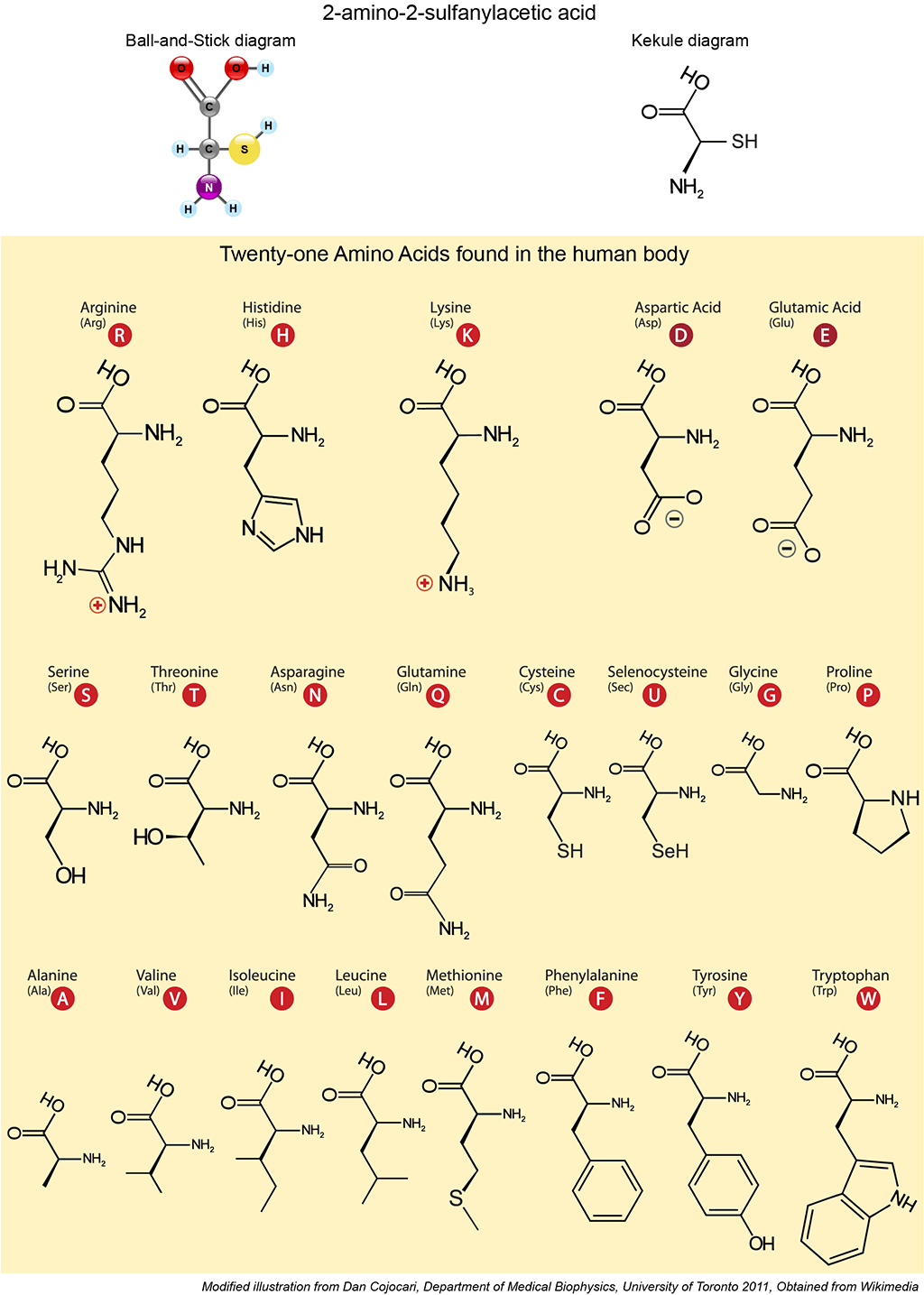
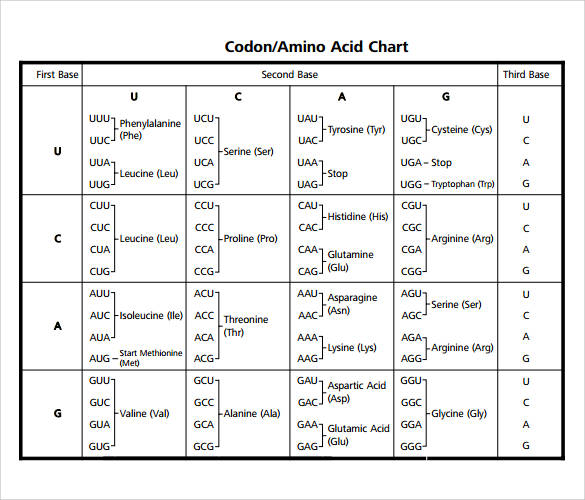
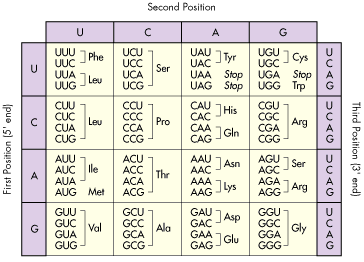
It lists 20 amino acids found in proteins along with the 64 available 3 letter symbols that correspond to each respectively. All amino acids contain both amino and carboxylic acids and in certain cases side chains. This carbon is designated as the α carbon alpha carbon.
How likely each amino acid is to be conserved and 2 if it is not conserved which amino acids are most likely to replace it. The amino acid chart provided on thedtu bioinformatics websiteis straightforward and offers up the 1 letter symbol and the dna codons. The properties of amino acids are determined by the functional substituents linked on the side chains which are most commonly referred to as r groups.
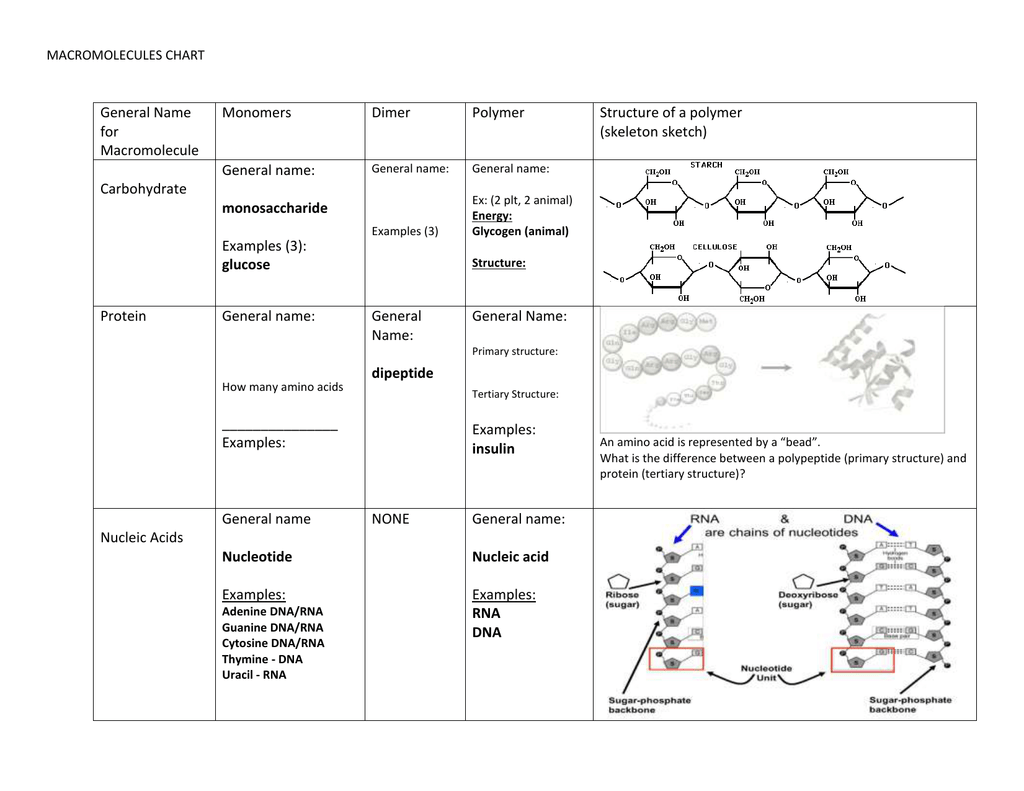
The r group for each of the amino acids will differ in structure electrical charge and polarity. There are basically four different classes of amino acids determined by different side chains. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins and all have the same basic structure differing only in the r group or side chain they have.
At the top of each column in the matrix is an amino acid that is boxed. Amino acids differ from each other with respect to their side chains which are referred to as r groups. A second abbreviation single letter is used in long protein structures consult the table on the left for structure names and abbreviations of 20 amino acids.